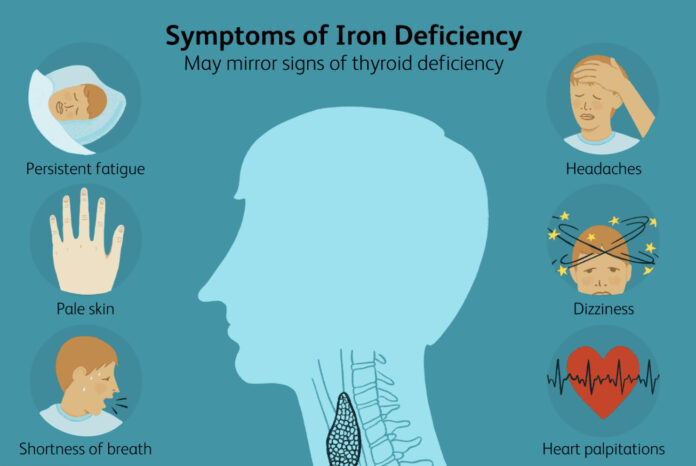
Iron helps red blood cells carry oxygen from the lungs to cells throughout the body. Iron also plays a role in many important functions of the body. Iron is a mineral necessary for the normal function of hemoglobin, a protein needed to transport oxygen in the blood. Iron also plays a role in many other important processes in the body. In this article, we’ll be discussing the things you should know about Iron.
How much Iron should you take?
Iron intake will depend on your age, diet, and gender:
- Infants
- 0 to 6 months: 0.27 milligrams (mg)
- 7 to 12 months: 11 mg
- Young children
- 1 to 3 years: 7 mg
- 4 to 8 years: 10 mg
- Male
- 9 to 13 years: 8 mg
- 14 to 18 years: 11 mg
- 19 years and older: 8 mg
- Female
- 9 to 13 years: 8 mg
- 14 to 18 years: 15 mg
- 19 to 50 years: 18 mg
- Age 51 and older: 8 mg
- During pregnancy: 27 mg
- When lactating between the ages of 14 and 18: 10 mg
- Lactating over the age of 19: 9 mg
Iron supplements may be helpful when people find it difficult to get enough iron through dietary measures alone, such as a plant-based diet. It is best to try to get enough in your diet only by eliminating or reducing factors that may hinder iron absorption and consuming iron-rich foods.
Benefits and side effects
Extra energy
Insufficient iron in the diet can affect how efficiently the body uses energy. Iron transports oxygen to the muscles and brain and is essential for both mental and physical performance. Low levels of iron may lead to poor concentration, irritability, and decreased stamina.
Healthy pregnancy
The production of blood and red blood cells increases dramatically during pregnancy, providing oxygen and nutrients to the growing fetus. Therefore, the demand for iron has also increased. Although the body usually maximizes iron absorption during pregnancy, insufficient iron intake or other factors that affect iron absorption can lead to iron deficiency.
Better physical performance
Iron deficiency in athletes can reduce athletic performance and impair immune system activity. A lack of hemoglobin can greatly reduce performance during physical exertion because it reduces the body’s ability to deliver oxygen to the muscles. Some experts recommend that female endurance athletes should get an extra 10 mg of iron per day.
Side effects
Iron is probably safe for most people when used in doses below the tolerated upper limit of 45 mg of elemental iron per day. It can cause side effects such as upset stomach, nausea, and vomiting. Taking iron supplements with food appears to reduce side effects.
Food rich in Iron
You can reduce your risk of iron deficiency anemia by choosing iron-rich foods such as:
- Red meat, pork, and poultry
- Seafood
- Beans
- Dark green leafy vegetables, such as spinach
- Dried fruit, such as raisins and apricots
- Iron-fortified cereals, bread, and pasta.
- Peas
Your body absorbs more iron from meat than other sources. If you choose not to eat meat, you may need to increase your intake of iron-rich plant foods to absorb the same amount of iron as someone who eats meat