Using Waters Laboratory Informatics Software’s comprehensive suite of solutions for instrument control, scientific data management, scientific search, network integration, and compliance management.
Our informatics solutions have helped market leaders in the pharmaceutical, environmental, food, beverage, and chemical materials industries save money, make better decisions, work more efficiently in the lab, and get their products to market faster.
Gradation of service
The primary goal of clinical laboratory professionals should be to provide the highest possible level of service to patients and those responsible for the patient’s care. A high-quality service will feature precise and timely analysis, clear and concise reporting, and convenient delivery to the customer’s preferred location and format. Quality today also incorporates such previously separate concepts as efficiency, effectiveness, diagnostic utility analysis, and decision support. As a result, integration into an all-encompassing EMR is now commonly regarded as a necessary outcome of service provision.
Current initiatives of the department of anatomic and clinical pathology include system integration for anatomic pathology. We collaborate closely with Nebraska Medicine Information Technology and our numerous commercial partners, such as LabLink, Cerner, and Dako, to automate or electronically transfer information between the laboratory and medical providers. This is the most important initiatives.
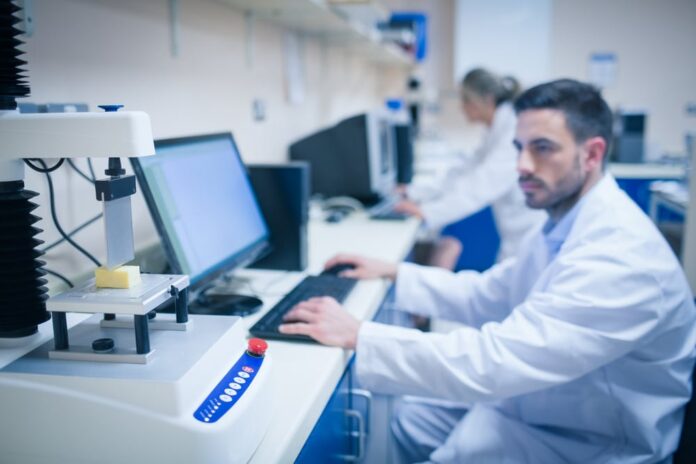
Informatics in the laboratory refers to the specific application of IT to the enhancement and expansion of laboratory processes.
Bioinformatics, chemo informatics, and health informatics are just a few of the other “informatics” fields that have seen explosive growth in recent years, contributing to its widespread adoption.
Laboratory informatics is often a central topic of study in graduate-level courses, especially those with a clinical bent. Some people consider laboratory automation to be synonymous with or even the same thing.
An increase in the need for laboratory automation is anticipated to drive uptake in the coming years. Increases in laboratory data production can be traced to recent technological advances in molecular genomics and genetic testing methods.
Market Trends in Laboratory Informatics:
The need for laboratory automation is growing as a result of the shortage of qualified laboratory professionals and the implementation of strategies to reduce or eliminate the use of human labor in laboratory procedures. Lab efficiency is improved and individual researchers are given more time to focus on important tasks when routine procedures are automated with the help of dedicated workstations and instrument-programming software. Automation not only improves documentation but also produces high-quality data.
Due to the exponential growth in data produced by laboratory equipment, there is a pressing need for efficient methods of data storage, processing, and dissemination.